How To Prevent Thrombosis And Protect Your Health
Table of Contents
ToggleOver the years, the prevalence of chronic diseases such as heart problems, diabetes, and obesity has surged. These conditions, combined with unhealthy lifestyle habits like poor diet and lack of exercise, have contributed to a significant rise in thrombosis cases. This life-threatening condition can strike anyone, and its impact varies widely depending on where the blood clot forms. Raising awareness about thrombosis and its complications can empower people to take preventive measures and seek timely treatment.
In this guide, we will explore the causes of thrombosis, its complications, and how you can protect yourself.
Common Risk Factors for Thrombosis
- Age over 60
- Chronic illnesses, including diabetes, cancer, high blood pressure, and heart valve disease
- A personal or family history of heart attacks, strokes, or blood clots
- Prolonged immobility, such as sitting for extended periods
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Paralysis in the leg
- Undergoing chemotherapy
Understanding these risk factors and having proper health insurance can help individuals identify their susceptibility and take necessary precautions to avoid complications. Let’s delve deeper into the specific forms of thrombosis and how they manifest.
Types of Thrombosis and Their Symptoms
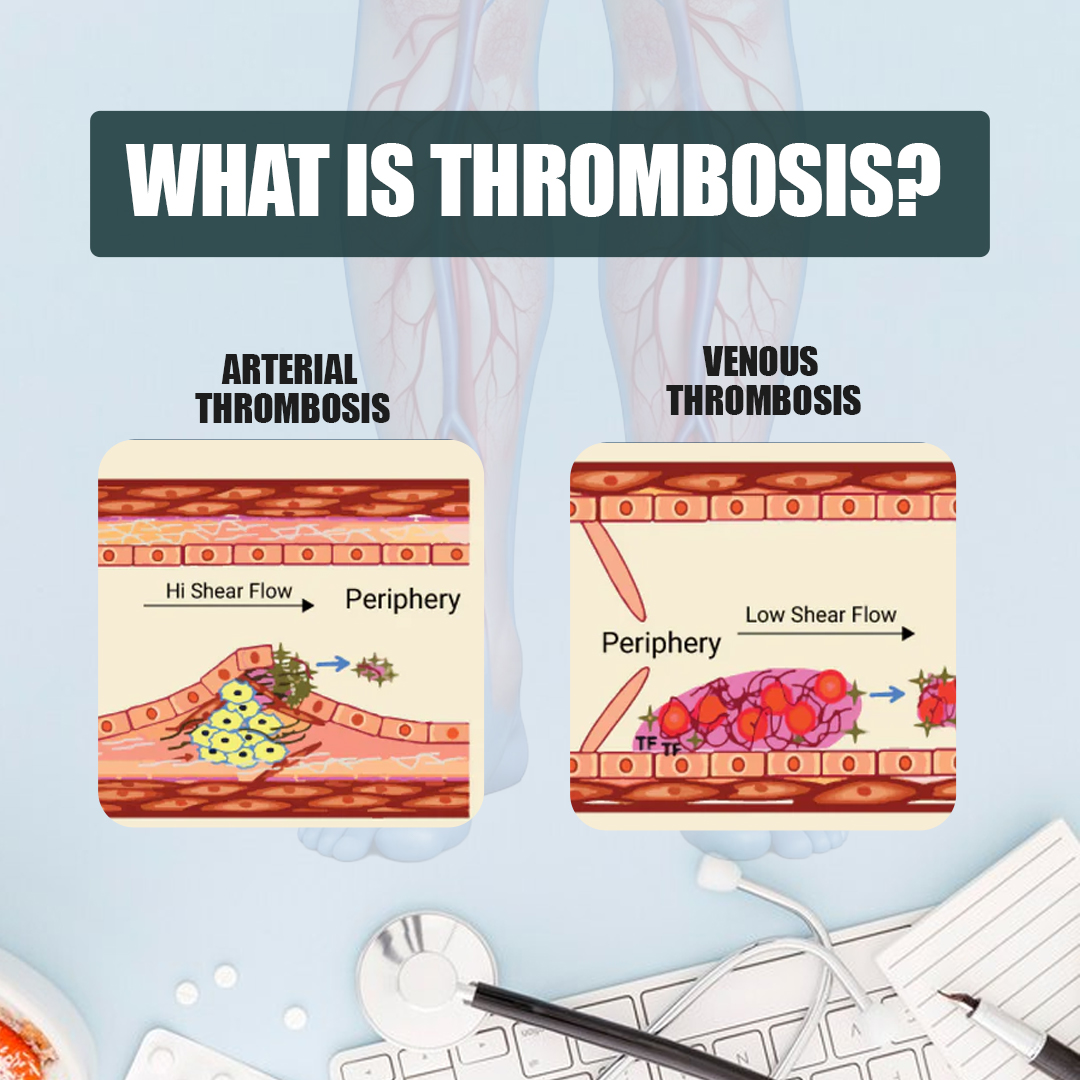
Thrombosis is broadly categorized into two types: arterial and venous. Each type has distinct causes and symptoms, and both require prompt attention.
Arterial Thrombosis
This type occurs when a blood clot forms in the arteries, which transport oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. Arterial thrombosis can lead to heart attacks, strokes, or other severe conditions.
Symptoms of Arterial Thrombosis
- Abrupt weakness or numbness may occur on one side of the body.
- Difficulty speaking or slurred speech.
- Confusion or trouble understanding others.
- Vision problems.
- Drooping of one side of the face.
- Inability to lift both arms.
Venous Thrombosis
When a blood clot forms in a vein that returns blood to the heart, then it is known as venous thrombosis. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a common form of venous thrombosis and can lead to pulmonary embolism if the clot travels to the lungs.
Symptoms of Venous Thrombosis
- Swelling in the affected limb, usually the leg
- Pain or tenderness, especially when standing or walking
- Discoloured or red skin over the affected area
- Warmth or heat in the affected area
- Visible swelling of veins under the skin
- A feeling of heaviness in the limb.
By recognizing these symptoms early, you can seek medical intervention and reduce the risk of life-threatening complications. Let’s explore how thrombosis impacts different parts of the body.
Complications of Thrombosis
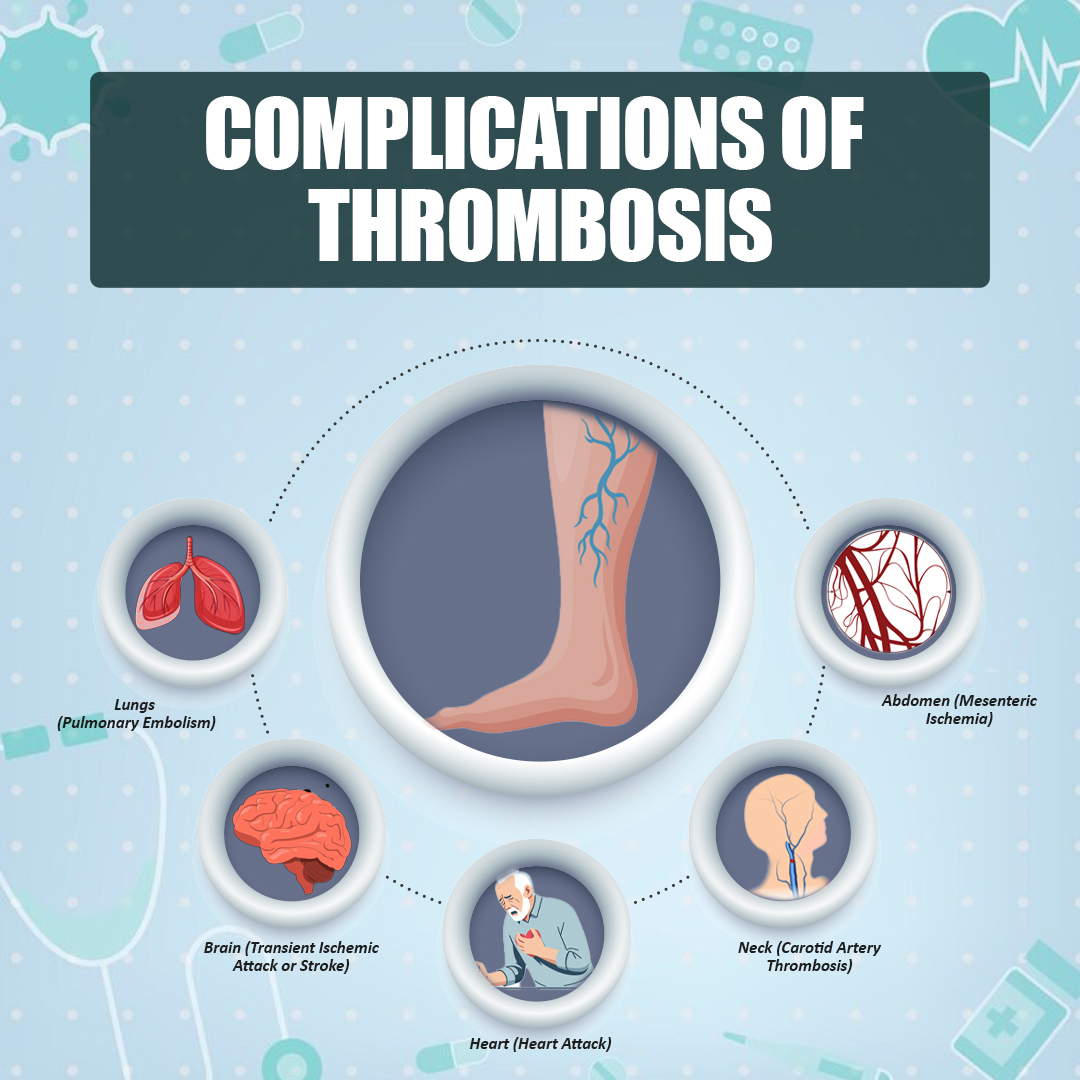
The location of a blood clot largely determines the complications of thrombosis. Below are some of the common sites and the associated risks:
1. Lungs (Pulmonary Embolism)
A pulmonary embolism is the result of a blood clot that makes its way to the lungs. This blocks blood flow and reduces oxygen levels, which can damage the lungs and strain the heart.
Symptoms
- Sharp pain in the chest or surrounding areas
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Sudden onset of rapid breathing
2. Brain (Transient Ischemic Attack or Stroke)
A clot in the brain can cause a transient ischemic attack or a stroke. While a TIA is temporary, it significantly raises the risk of a full stroke later.
Symptoms
- Confusion or sudden changes in behavior
- Slurred or unclear speech
- Drooping of one side of the face
3. Heart (Heart Attack)
A heart attack can result from a clot that stops blood flow to the heart, killing heart muscle tissue.
Symptoms
- Intense chest pain (angina)
- Pain radiating to the arms, neck, or back
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue or dizziness
4. Neck (Carotid Artery Thrombosis)
Blood clots in the carotid arteries can limit oxygen-rich blood flow to the brain, increasing the likelihood of a TIA or stroke.
Symptoms
- Sudden, severe headache
- Loss of balance or dizziness
- Difficulty speaking or slurred speech.
5. Abdomen (Mesenteric Ischemia)
Thrombosis in the abdominal region can lead to restricted blood flow in the digestive system, potentially resulting in organ damage.
Symptoms
- Severe abdominal pain after eating
- Bloating, nausea, or vomiting
- Diarrhoea with possible blood
- Loss of appetite and weight loss.
Recognizing the complications of thrombosis highlights the importance of taking preventive action. Let’s shift focus to practical measures and lifestyle changes that can help reduce your risk.
Preventive Measures

Preventing thrombosis begins with understanding your risk factors and making proactive lifestyle changes. Here’s what you can do:
- Stay Physically Active: Frequent exercise lowers the risk of blood clots and enhances circulation. Simple exercises like stretching or walking can have a significant impact.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity increases the strain on your circulatory system, making you more susceptible to thrombosis. Make eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins a priority.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting: If your job requires sitting for long periods, take breaks to stand, stretch, or walk around. This reduces blood stagnation and prevents clot formation.
- Quit Smoking: Tobacco use damages blood vessels and significantly raises the risk of thrombosis. If necessary, get expert assistance to break the habit.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: If you have diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol, follow your doctor’s advice to keep these conditions under control.
Adopting preventive measures is a powerful step in reducing your risk of thrombosis, but early diagnosis plays an equally vital role.
Why Early Diagnosis Is Critical
Timely diagnosis can save lives by preventing the progression of thrombosis into more severe conditions. If you experience any symptoms related to thrombosis, consult a healthcare professional immediately. Routine health check-ups can also help identify risk factors early and provide opportunities for preventive care. Please contact your insurer for financial security.
If you have not taken health insurance yet, let’s explore how Insura can make your life a little easier.
How Insura Can Help You?

Dealing with the complications of thrombosis can lead to high medical expenses. Insura offers comprehensive health and critical illness insurance plans tailored to your needs. These policies cover hospital bills, medications, and even specialised treatments, ensuring that you receive quality care without financial stress.
Benefits of Choosing Insura
- Extensive Coverage: Access a network of top medical facilities.
- Plans That Are Affordable: Look for an insurance that meets your spending limit.
- Hassle-Free Claims: Enjoy quick and easy claims processing.
- 24/7 Support: Get assistance whenever you need it.
Stay prepared for uncertain times with Insura and protect your health and finances.
Take Action Today
Thrombosis is a silent threat that can have devastating consequences if left unchecked. By understanding the causes and complications, you can take proactive steps to safeguard your health. Make lifestyle changes, recognize early symptoms, and prioritize routine medical check-ups. Most importantly, invest in a reliable health insurance plan to ensure access to quality care when you need it most.
Don’t wait for a crisis—act now to protect yourself and your loved ones from the risks of thrombosis.
FAQ's
How can thrombosis be prevented?
Thrombosis can be prevented by staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and managing chronic conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure.
How to avoid thrombosis on long flights?
Avoid thrombosis on long flights by staying hydrated, wearing compression stockings, and moving or stretching your legs regularly during the flight.
What to drink to prevent blood clots?
Drinking water, green tea, or natural juices like cranberry juice may help improve circulation and prevent blood clots.
What are the 3 factors that lead to thrombosis?
The three factors are hypercoagulability (blood clotting disorders), stasis (prolonged immobility), and vessel wall injury.
Which fruit is best for blood thinner?
Citrus fruits like oranges and grapefruits, rich in vitamin C, can support blood thinning and improve circulation.
